- Sudeck’s Atrophy
- Causalgia
- Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD)
- Shoulder-Hand Syndrome
- Post-Traumatic Dystrophy
- Reflex Neurovascular Dystrophy
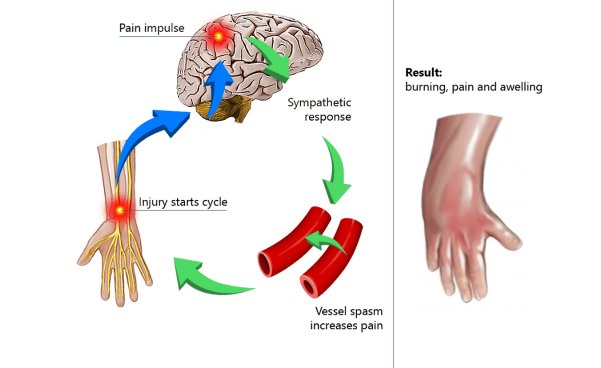
Causes of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
The exact cause of CRPS is not fully understood. It typically develops after an injury or surgery but can also appear spontaneously.
- CRPS Type I: Triggered by injuries like sprains, fractures, or surgery without direct nerve damage.
- CRPS Type II: Caused by a confirmed nerve injury.
Proposed mechanisms include:
- Nervous System Overactivity: Nerves send excessive pain signals even after the initial injury has healed.
- Inflammation: Persistent swelling irritates nerves and prolongs pain.
- Immune System Role: An overactive immune response may contribute to inflammation.
- Blood Flow Changes: Altered circulation leads to color and temperature changes in the skin.
Symptoms of CRPS
CRPS can present differently in each person. Common symptoms include:
- Intense Pain: Burning, throbbing, or aching pain disproportionate to the original injury.
- Swelling: Puffiness and enlargement of the affected area.
- Skin Color and Temperature Changes: Red, blue, or pale skin; warmer or cooler compared to the other limb.
- Allodynia (Painful Sensitivity): Severe pain from light touch or temperature changes.
- Hair and Nail Changes: Faster or slower than normal growth.
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: Reduced mobility, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected limb.
- Muscle Weakness and Atrophy: Decreased use can lead to shrinking muscles.
- Abnormal Sweating or Movement: Tremors, jerks, or unusual movements in the limb.
Prognosis of CRPS
The long-term outlook for CRPS varies:
- Some patients improve within six months.
- Others continue to experience pain and disability for years.
- Recurrence is common, especially in younger patients and children. Relapses may occur spontaneously or after new injuries, surgeries, or emotional stress.
- Recurrence can affect the same limb or appear in a different one.
With proper treatment and ongoing support, many patients improve function and quality of life, though some may need workplace or lifestyle adjustments.
Diagnosis of CRPS
There is no single diagnostic test. Doctors rely on:
- Medical history and symptom review
- Physical exam for swelling, color, temperature, and touch sensitivity
- Imaging (X-ray, MRI, bone scan) to rule out other conditions
- Specialist referral for complex cases
Pain Medicine Interventions
Several pain management approaches can help reduce CRPS symptoms:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: NSAIDs or acetaminophen for mild pain.
- Prescription Medications: Opioids for short-term severe pain (with caution).
- Antidepressants and Anticonvulsants: Amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin, pregabalin for nerve-related pain.
- Topical Treatments: Lidocaine patches or capsaicin cream.
- Nerve Blocks: Injections that temporarily block abnormal pain signals.
- Spinal Cord Stimulation: Electrical pulses delivered to the spine to reduce pain signals.
Treatment of CRPS
CRPS care usually involves a multidisciplinary plan, including:
- Physical Therapy: Maintains movement and prevents stiffness.
- Occupational Therapy: Teaches strategies for daily activities.
- Nerve Blocks or Spinal Cord Stimulation: For patients with severe pain.
- Psychological Support: Counseling and stress management, since CRPS affects mental health.
Procedure Videos
Sympathetic Nerve Block Injection
Stellate Ganglion Block
Spinal Cord Stimulation
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wzpk0U4KPn4https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z0xjpegaR6Q
Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pu9QJLVTGe8https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y06hSY_jAS0&t=1s
References
- ACEP Now. (2016, December 14). What emergency physicians need to know about complex regional pain syndrome. Retrieved from https://www.acepnow.com/article/emergency-physicians-need-know-complex-regional-pain-syndrome/
- Arizona Pain. (n.d.). Complex regional pain syndrome. Retrieved from https://arizonapain.com/conditions/complex-regional-pain-syndrome/
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (n.d.). Complex regional pain syndrome. Retrieved from https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/complex-regional-pain-syndrome#toc-how-is-complex-regional-pain-syndrome-diagnosed-and-treated-
- Treating Pain. (n.d.). Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). Retrieved from https://www.treatingpain.com/conditions/crps/
- UpToDate. (n.d.). Complex regional pain syndrome in adults: Treatment, prognosis, and prevention. Retrieved from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complex-regional-pain-syndrome-in-adults-treatment-prognosis-and-prevention?search=complex%20regional%20pain%20syndrome&topicRef=5628&source=related_link#H393243402