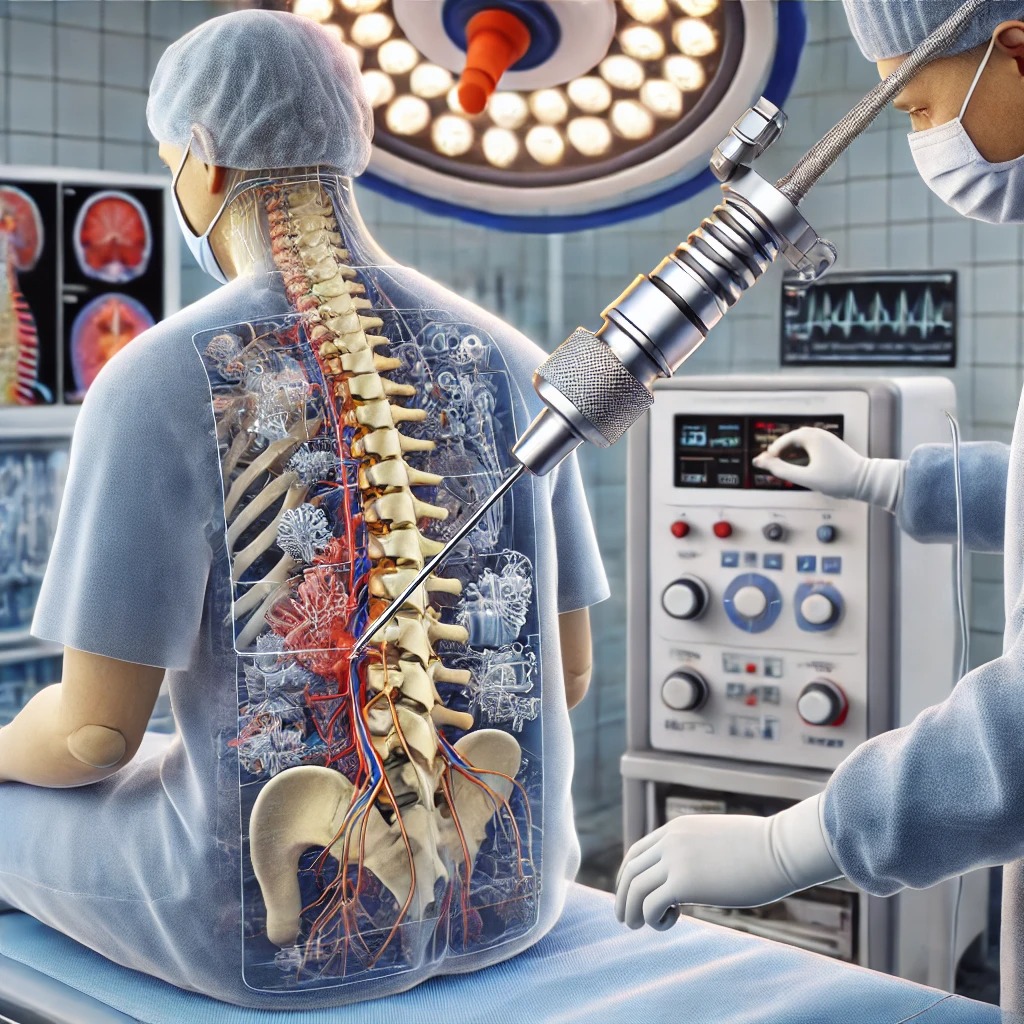
What is Radiofrequency Rhizotomy?
Radiofrequency rhizotomy is a minimally invasive procedure most commonly used to treat nerve pain originating in the spine. Rhizotomy, also called neurotomy or ablation, is a procedure that purposefully damages nerve fibers that are responsible for sending pain signals to the brain. Radiofrequency is the method by which the targeted nerve fibers are destroyed; radio waves generate heat energy which damages the nerves. Radiofrequency rhizotomy can provide immediate pain relief that typically lasts 6-12 months, until the nerve heals and is able to transmit pain once again.
Radiofrequency rhizotomy can target chronic neck, lower back, or sacroiliac pain originating from degenerative facet joints, the hinge-like joints that hold vertebrae together in the spinal column. Small nerves receive sensation from these joints and send pain signals to the brain. Radiofrequency rhizotomy can be an effective method to treat neuropathic neck and back pain from arthritis, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and other degenerative spine conditions. Radiofrequency rhizotomy can also be used to treat nerve pain associated with conditions outside of the spine, including knee or hip arthritis, trigeminal neuralgia, postherpetic neuralgia, and spasticity, such as in cerebral palsy.
Procedure: Radiofrequency Rhizotomy
Radiofrequency rhizotomy is performed under general anesthesia or IV sedation. If the procedure involves your spine, you will be lying face down. Your surgeon will use local anesthetic to numb the procedure area. A small needle is inserted into the appropriate area, using fluoroscopy (x-ray) to guide placement. Placement may also be verified by your surgeon stimulating the target nerve and observing a response. Highly focused heat energy is then applied to the affected nerve(s), causing damage and preventing the transmission of pain.
Videos
Post-operative Care for Radiofrequency Rhizotomy
Following the procedure, patients can be discharged the same day. You can return to normal activities as you feel comfortable. Full recovery should occur within 3-4 weeks.
Goals of Radiofrequency Rhizotomy
Pain relief
Improvement in spasticity
Benefits of Radiofrequency Rhizotomy
Benefits of radiofrequency rhizotomy include:
- Relief of neck and back pain
- Minimally invasive
- Facilitates physical therapy
Side Effects
- Pain, swelling, bruising at surgical site
- Risk of bleeding
- Risk of infection
- Risk of nerve damage that may result in numbness, bowel or bladder incontinence, paralysis
Resources
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/24903-rhizotomy